Openpyxl is a Python library that reads and writes Excel files (with the extensions xlsx/xlsm/xltx/xltm). Python openpyxl module allows the program to read and modify Excel files.
For example, a user will have to go through hundreds of rows of data and select a few handful of information to make minor changes based on some criterion. These activities can be completed quickly and easily with the Openpyxl module.
Installation:
sudo pip3 install openpyxl
Let us take an example of demo.xlsx excel spreadsheet as shown below:
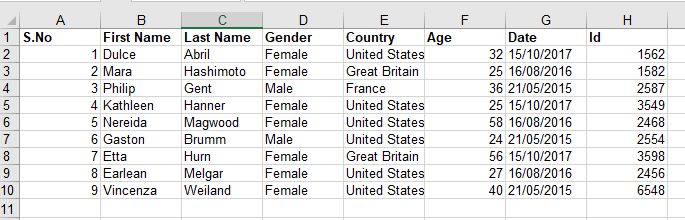
Program for Reading an Excel File using openpyxl Module in Python
Example1: Python Code for printing the specified cell value
Approach:
- Import openpyxl module using the import keyword.
- Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file.
- Pass the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook() function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable.
- Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable.
- Select the any random cell of the excel sheet by passing some random row_no & col_no as arguments to the cell() function and store it in a variable.
- Print value of above-given cell object using the value attribute.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import openpyxl module using the import keyword import openpyxl # Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file. file_path = "demo.xlsx" # Pass the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook() # function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable. work_book = openpyxl.load_workbook(file_path) # Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable. actve_sheet = work_book.active # Select the any random cell of the excel sheet by passing some random # row_no & col_no as arguments to the cell() function and store it in a variable. gvn_cell = actve_sheet.cell(row = 1, column = 2) # Print value of above given cell object using the value attribute print(gvn_cell.value)
Output:
First Name
Example2: Python Code for printing total no of rows in Excel sheet
Approach:
- Import openpyxl module using the import keyword.
- Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file.
- Pass the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook() function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable.
- Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable.
- Print the total number of rows present in the above given Excel sheet by using the max_row attribute.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import openpyxl module using the import keyword
import openpyxl
# Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file.
file_path = "demo.xlsx"
# Pass the the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook()
# function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable.
work_book = openpyxl.load_workbook(file_path)
# Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable.
actve_sheet = work_book.active
# Print the total number of rows present in the above given Excel
# sheet by using the max_row attribute
print("Total no of rows present in the above given Excel sheet = ", actve_sheet.max_row)
Output:
Total no of rows present in the above given Excel sheet = 10
Example3: Python Code for printing total no of columns in Excel sheet
Approach:
- Import openpyxl module using the import keyword.
- Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file.
- Pass the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook() function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable.
- Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable.
- Print the total number of columns present in the above given Excel sheet by using the max_column attribute.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import openpyxl module using the import keyword
import openpyxl
# Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file.
file_path = "demo.xlsx"
# Pass the the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook()
# function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable.
work_book = openpyxl.load_workbook(file_path)
# Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable.
actve_sheet = work_book.active
# Print the total number of columns present in the above given Excel
# sheet by using the max_column attribute
print("Total no of columns present in the above given Excel sheet = ", actve_sheet.max_column)
Output:
Total no of columns present in the above given Excel sheet = 8
Example4: Python Code for printing all the columns of the Excel sheet
Approach:
- Import openpyxl module using the import keyword.
- Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file.
- Pass the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook() function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable.
- Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable.
- Get the total number of columns present in the above given Excel sheet by using the max_column attribute and store it in another variable.
-
Iterate from 1 to the above total number of columns using the for loop.
-
Get the iterator number column of the 1st row using the cell() function.
-
Print the column name using the value attribute.
-
The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import openpyxl module using the import keyword
import openpyxl
# Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file.
file_path = "demo.xlsx"
# Pass the the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook()
# function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable.
work_book = openpyxl.load_workbook(file_path)
# Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable.
actve_sheet = work_book.active
# Get the total number of columns present in the above given
# Excel sheet by using the max_column attribute and store it in another variable.
tot_cols = actve_sheet.max_column
# Iterate from 1 to the above total number of columns using the for loop
for itr in range(1, tot_cols + 1):
# Get the iterator number column of the 1st row using the cell() function
cellobject = actve_sheet.cell(row = 1, column = itr)
# Print the column name using the value attribute
print(cellobject.value)
Output:
S.No First Name Last Name Gender Country Age Date Id
Example5: Python Code for printing the 2nd(any col) column values
Below is the implementation:
# Import openpyxl module using the import keyword
import openpyxl
# Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file.
file_path = "demo.xlsx"
# Pass the the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook()
# function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable.
work_book = openpyxl.load_workbook(file_path)
# Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable.
actve_sheet = work_book.active
# Get the total number of columns present in the above given
# Excel sheet by using the max_column attribute and store it in another variable.
tot_cols = actve_sheet.max_column
# Iterate from 1 to the above total number of columns using the for loop
for itr in range(1, tot_cols + 1):
# Get the iterator number of rows of the 2nd column using the cell() function
cellobject = actve_sheet.cell(row = itr, column = 2)
# Print the given column value using the value attribute
print(cellobject.value)
Output:
First Name Dulce Mara Philip Kathleen Nereida Gaston Etta
# Import openpyxl module using the import keyword
import openpyxl
# Take a variable and initialize it with the path of the file.
file_path = "demo.xlsx"
# Pass the the above file path as an argument to the load_workbook()
# function to create a workbook object and store it in a variable.
work_book = openpyxl.load_workbook(file_path)
# Choose the active sheet using the active attribute and store it in another variable.
actve_sheet = work_book.active
# Get the total number of columns present in the above given
# Excel sheet by using the max_column attribute and store it in another variable.
tot_cols = actve_sheet.max_column
# Iterate from 1 to the above total number of columns using the for loop
for itr in range(1, tot_cols + 1):
# Get the iterator number of columns of the 3rd row using the cell() function
cellobject = actve_sheet.cell(row = 3, column = itr)
# Print the given row value using the value attribute
print(cellobject.value)
Output:
2 Mara Hashimoto Female Great Britain 25 16/08/2016 1582