The Xlsx module of the Python programming language is one of the most important libraries for helping us plot line charts in an Excel worksheet. The Python Xlsx library can do mathematical operations, display charts in Excel, import data, write data, and much more.
It is important for users to determine a chart object for the necessary chart type before inserting the chart sheet in Excel in order to make a line chart in Excel using Python. Once the Python objects for the column charts have been defined, all that is needed to construct a line chart in Excel in Python is to enter the data and insert the same into the sheet objects. This page provides instructions and examples for adding a line chart to an Excel worksheet using the Python Xlsx library.
Insert Line Charts in Excel Sheet Using XLSX Module
Charts are made up of a series of one or more data points. The series is made up of references to cell ranges. To plot the charts on an excel sheet, first create a chart object of the desired chart type ( i.e Stock chart, etc.). After generating chart objects, insert data into them before adding them to the sheet object.
Line Chart:
A line chart is a graphical representation of an asset’s historical price activity in which a sequence of data points are connected by a continuous line. This is the most basic sort of chart used in finance, and it typically merely shows the closing prices of a security over time. Line charts can be used for any timescale, however they are most commonly used to show daily price movements.
Install the xlsxwriter using the below code
pip install xlsxwriter
Looking in indexes: https://pypi.org/simple, https://us-python.pkg.dev/colab-wheels/public/simple/
Collecting xlsxwriter
Downloading XlsxWriter-3.0.3-py3-none-any.whl (149 kB)
|████████████████████████████████| 149 kB 5.0 MB/s
Installing collected packages: xlsxwriter
Successfully installed xlsxwriter-3.0.3
Program to Plot Line Charts in Excel Sheet using XlsxWriter module in Python
Below is the full approach to plot the line charts in Excel Sheet using XlsxWriter
Approach:
- Import the xlsxwriter library using the import function.
- Pass the excel file path to the Workbook() function of xlsxwriter which is the file we want to create and store in a variable.
- Create the new Worksheet using the add_worsheet() function and apply it to the above workbook object and store it in a variable.
- Create a new Format object to format cells in spreadsheets using the add_format() method and apply it to the above workbook object.
- Here, we created a bold format object.
- Add the worksheet data that the charts will use.
- Write a row of heading data starting with ‘A1’ in the bold format using the write_row() function and apply on the above worksheet object by passing the argument rowNumber,headings list,and format.
- Write the column data that is starting from ‘A2′,’B2′,’C2’ using the write_coulmn() function and pass data as argument to it.
- Write a column of data starting from ‘A2’, ‘B2’, ‘C2’ respectively .
- Using the add_chart() method, create a chart object that can be added to a worksheet.
- Pass the type of chart as an argument to the add_chart() function and apply it to the above workbook object
- Using the add series() method, you can add a data series with a gradient pattern to a chart.
- The gap is used to highlight the patterns.
- Add the first series data using the add_series() function.
- Configuring the second series.
- Take note of the usage of different syntax to declare ranges [sheetname, first row, first col, last row, last col].
- Set the title to the chartObject using the set_title() function by passing the chart title name as value and key as “name” (Here the arguments are object).
- Label the x-axis using the set_x_axis() function by passing the Sem Number as value and key as “name” (Here the arguments are object).
- Label the y axis using the set_x_axis() function by passing the Data length as value and key as “name” (Here the arguments are object).
-
Set the style of chart using the set_style() function.
- Add a chartObject to the worksheet with the provided offset values in the top-left corner of a chartObject that is anchored to cell D2.
- Close the workbook Object using the close() function.
Below is the Implementation:
# Import the xlsxwriter library using the import function
import xlsxwriter
# Pass the excel file path to the Workbook() function of xlsxwriter
# which is the file we want to create and store it in a variable
workbookObj = xlsxwriter.Workbook('chartLine.xlsx')
# Create the new Worksheet using the add_worsheet() function and
# apply it to the above workbook object and store it in a variable
newWorksheet = workbookObj.add_worksheet()
# Create a new Format object to format cells in spreadsheets using the add_format() method and apply it to the above workbook object.
# Here, we created a bold format object. .
boldFormat = workbookObj.add_format({'bold': 1})
# Add the worksheet data that the charts will use.
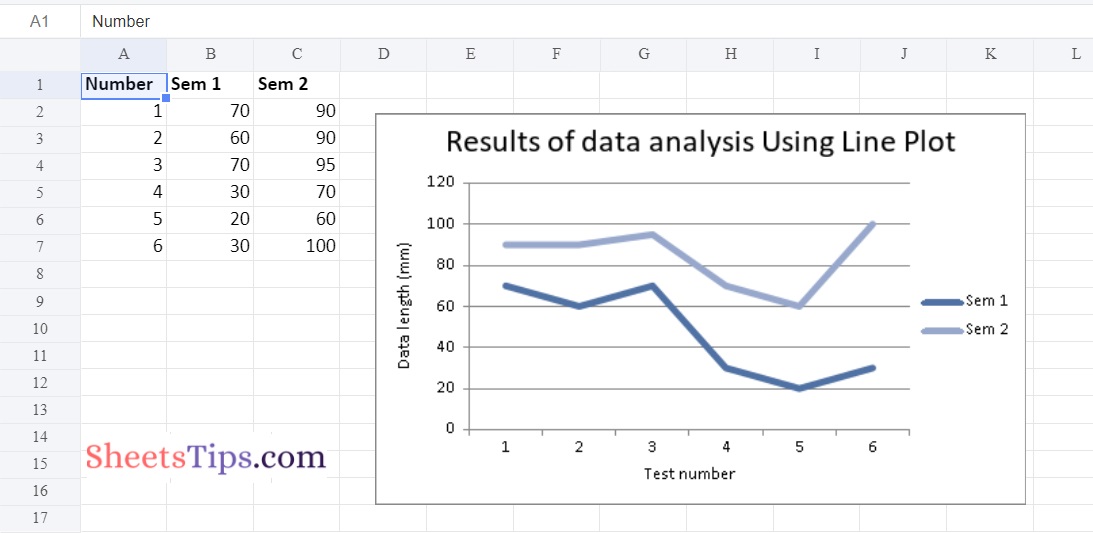
headingsData = ['Number', 'Sem 1', 'Sem 2']
worksheetData = [
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[70, 60, 70, 30, 20, 30],
[90, 90, 95, 70, 60, 100]
]
# Write a row of heading data starting with 'A1' in bold format using the write_row() function
# and apply on the above worksheet object
# by passing the argument rowNumber,headings list,and format.
newWorksheet.write_row('A1', headingsData, boldFormat)
# Write the column data that is starting from 'A2','B2','C2'
# using the write_coulmn() function
# and pass data as argument to it
# Write a column of data starting from
# 'A2', 'B2', 'C2' respectively .
newWorksheet.write_column('A2', worksheetData[0])
newWorksheet.write_column('B2', worksheetData[1])
newWorksheet.write_column('C2', worksheetData[2])
# Using the add_chart() method, create a chart object that can be added to a worksheet.
# Pass the type of chart as an argument to the add_chart() function and apply it to the above workbook object
chartObject = workbookObj.add_chart({'type': 'line'})
# Using the add series() method, you can add a data series with a gradient pattern to a chart.
# The gap is used to highlight the patterns.
# Add the first series data using the add_series() function
chartObject.add_series({
'name': '= Sheet1 !$B$1',
'categories': '= Sheet1 !$A$2:$A$7',
'values': '= Sheet1 !$B$2:$B$7'
})
# Configuring the second series.
# Take note of the usage of different syntax to declare ranges.
#[sheetname, first row, first col, last row, last col]
chartObject.add_series({
'name': ['Sheet1', 0, 2],
'categories': ['Sheet1', 1, 0, 6, 0],
'values': ['Sheet1', 1, 2, 6, 2],
})
# Set the title to the chartObject using the set_title() function
# by passing the chart title name as value and key as "name" (Here the arguments are object)
chartObject.set_title ({'name': 'Results of data analysis Using Line Plot'})
# Label the x axis using the set_x_axis() function by passing the Sem Number as value and key as "name" (Here the arguments are object)
chartObject.set_x_axis({'name': 'Test number'})
# Label the y axis using the set_x_axis() function by passing the Data length as value and key as "name" (Here the arguments are object)
chartObject.set_y_axis({'name': 'Data length (mm)'})
# set the style of chart using the set_style() function
chartObject.set_style(11)
# Add a chartObject to the worksheet with the provided offset values in the top-left corner of a chartObject that is anchored to cell D2.
newWorksheet.insert_chart('D2', chartObject,
{'x_offset': 25, 'y_offset': 10})
# Close the workbook Object using the close() function.
workbookObj.close()
Output:
One of the robust programming languages that enable us to automate Excel in Python. It features a number of modules that allow us to easily build a variety of things without opening any Excel files. Keep checking SheetsTips.Com for more information on automating Excel using Python.