To export different data frames to different Excels using Python, we must use the xlsxwriter function offered by Pandas. ExcelWriter() is a class that allows DataFrame objects to be written into Microsoft Excel sheets. ExcelWriter() supports the creation of text, integers, strings, and formulas and It may also be used for several spreadsheets. Let us explore everything about ExcelWriter() and how to write pandas data frames for multiple sheets in an excel file. Read further to find out more.
ExcelWriter() Function
Pandas have a function called xlsxwriter for this. ExcelWriter() is a class that allows DataFrame objects to be written into Microsoft Excel sheets. ExcelWriter() supports the creation of text, integers, strings, and formulas. It can also be used for several spreadsheets.
Syntax:
pandas.ExcelWriter(path, date_format=None, mode='w')
Parameters
path: It is the path of the xls or xlsx or ods file given as input in a string format.
date_format: It is the Date format string for Excel files (for example, ‘YYYY-MM-DD’). The default is None.
mode: It may be {‘w’, ‘a’}. The default is ‘w’. It is the file mode that we want to use(write/append). Append does not support fsspec URLs.
Python to_excel() Function:
To export the DataFrame to an excel file, use the to_excel() method. The target file name must be specified when writing a single object to an excel file. If we wish to write to multiple sheets, we must first create an ExcelWriter object with the target filename and then indicate the sheet in the file we want to write to. The unique sheet_name can also be used to write multiple sheets. All modifications made to the data written to the file must be saved.
Syntax:
DataFrame.to_excel(excel_writer, sheet_name='Sheet1', index=True)
Parameters
excel_writer: It is the file path/file, or ExcelWriter object (new or existing)
sheet_name: It is the name of the sheet containing DataFrame. ‘Sheet1’ by default. It is in string format.
index: It is used to write row names (index). This is boolean and True by default.
Python Code to Write Pandas DataFrames to Multiple Excel Sheets
Approach:
- Import the pandas module using the import keyword
- Create a first dataframe passing some random a dictionary(where values are stored as a list) as an argument to the DataFrame() function of the pandas module.
Store it in a variable. - Create a second dataframe passing some random a dictionary(where values are stored as a list)
as an argument to the DataFrame() function of the pandas module.
Store it in another variable. - Similarly, create the third dataframe and store it in another variable.
- Print the given first dataframe.
Print the given second dataframe.
Print the given third dataframe. - Create an excel writer object by passing the file path as an argument to the ExcelWriter() function
- Pass the above excel writer object, sheet name, index=False to the use to_excel() function
to store the above-given dataframes in specified sheets. - The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import the pandas module using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Create a first dataframe passing some random a dictionary(where values are stored as a list)
# as an argument to the DataFrame() function of the pandas module.
# Store it in a variable.
gvn_datafrme1 = pd.DataFrame({'StudentNames': ['John', 'Nick', 'Mary',
'Sam', 'virat', 'victoria'],
'Marks': [32, 75, 90, 85, 50, 65]})
# Create a second dataframe passing some random a dictionary(where values are stored as a list)
# as an argument to the DataFrame() function of the pandas module.
# Store it in another variable.
gvn_datafrme2 = pd.DataFrame({'Websites': ['SheetsTips', 'Python-Programs', 'BtechGeeks',
'PythonArray', 'Chrome', 'Facebook'],
'About': ['Excel', 'Python codes', 'All courses', 'Arrays', 'Browser', 'Social-media App']})
# Similarly create the third dataframe and store it in another variable.
gvn_datafrme3 = pd.DataFrame({'Countries': ['India', 'USA', 'France',
'Australia', 'Srilanka', 'China'],
'Capitals': ['New Delhi', 'Washington.DC', 'Paris', 'Canberra', 'Colombo', 'Beijing']})
# Print the given first dataframe
print(gvn_datafrme1)
print()
# Print the given second dataframe
print(gvn_datafrme2)
print()
# Print the given third dataframe
print(gvn_datafrme3)
# Create an excel writer object by passing the filepath as an argument to the ExcelWriter() function
with pd.ExcelWriter("Output_Excelfile.xlsx") as xlwriter:
# Pass the above excel writer object, sheet name, index=False to the use to_excel() function
# to store the above given dataframes in a specified sheets.
gvn_datafrme1.to_excel(xlwriter, sheet_name="StudentNames&Marks", index=False)
gvn_datafrme2.to_excel(xlwriter, sheet_name="Websites", index=False)
gvn_datafrme3.to_excel(xlwriter, sheet_name="Countries", index=False)
Output:
StudentNames Marks
0 John 32
1 Nick 75
2 Mary 90
3 Sam 85
4 virat 50
5 victoria 65
Websites About
0 SheetsTips Excel
1 Python-Programs Python codes
2 BtechGeeks All courses
3 PythonArray Arrays
4 Chrome Browser
5 Facebook Social-media App
Countries Capitals
0 India New Delhi
1 USA Washington.DC
2 France Paris
3 Australia Canberra
4 Srilanka Colombo
5 China Beijing
Output Image:
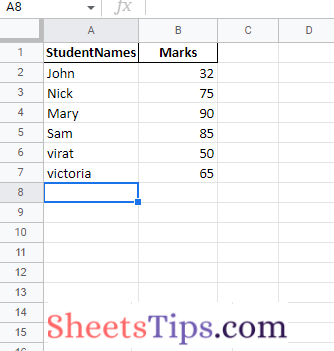
Explanation:
Here, multiple sheets were saved in the specified location in an Excel file.
Another way of storing the Dataframe in an Existing Excel file using ExcelWriter() function
Here we append a new excel sheet to the already existing Excel file instead of creating a new file.
We now use the above Output_Excelfile and append a new sheet to that file by passing the argument mode as ‘a’ (append).
Using mode ‘a,’ the new sheet will be added as the last sheet in the existing excel file.
Approach:
- Import the pandas module using the import keyword
- Create a dataframe passing some random a dictionary(where values are stored as a list) as an argument to the DataFrame() function of the pandas module.
- Store it in a variable.
Print the given dataframe. - Create an excel writer object by passing the filepath, mode as append, and engine=”openpyxl” as an argument to the ExcelWriter() function.
- Here it is used to append the given 4th dataframe as a last sheet in the existing Excel file
Pass the above excel writer object, sheet name, index=False to the use to_excel() function
to store the above-given dataframe in a specified sheet. - Here we are appending a new sheet(Employee&salary) to the already existing Output_Excelfile
Below is the implementation:
# Import the pandas module using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Create a dataframe passing some random a dictionary(where values are stored as a list)
# as an argument to the DataFrame() function of the pandas module.
# Store it in a variable.
gvn_datafrme4 = pd.DataFrame({'Employee': ['Danny', 'Sindhu', 'Steve',
'Rosy', 'Alex', 'Diya'],
'Salary': [25000, 50000, 40000, 80000, 100000, 60000]})
# Print the given dataframe
print(gvn_datafrme4)
# Create an excel writer object by passing the filepath, mode as append and engine="openpyxl" as an argument
# to the ExcelWriter() function.
# Here it is used to append the given 4th dataframe as a last sheet in the existing Excel file
with pd.ExcelWriter("Output_Excelfile.xlsx", mode="a", engine="openpyxl") as writer:
# Pass the above excel writer object, sheet name, index=False to the use to_excel() function
# to store the above given dataframe in a specified sheet.
# Here we are appending a new sheet(Employee&salary) to the already existing Output_Excelfile
gvn_datafrme4.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Employee&salary", index=False)
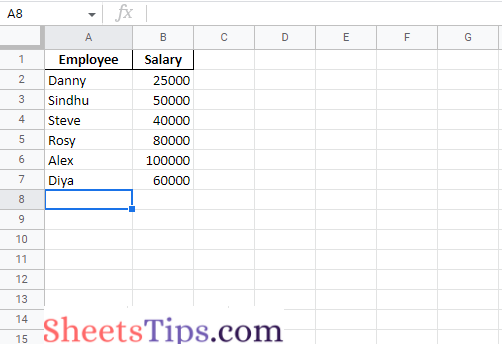
Output:
Employee Salary 0 Danny 25000 1 Sindhu 50000 2 Steve 40000 3 Rosy 80000 4 Alex 100000 5 Diya 60000
The Pandas ExcelWriter () function is one of the most useful functions for writing data frames for multiple sheets. But to get this done in Excel, make sure you are installing xlsxwriter.