In this article, we are going to compare the two excel files columns in Python and their column numbers respectively.
Prerequisites:
Program to Compare Excel Files in Python
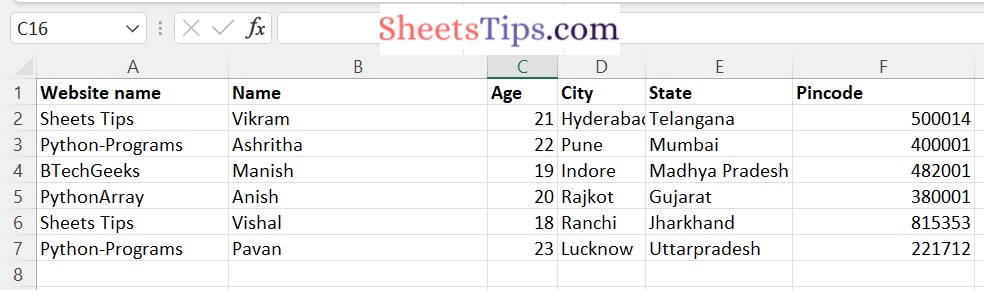
sampleExcelFile1.xlsx:
This file contains 6 columns with 6 unique student details. The following are the column names:
- Website name
- Name
- Age
- City
- State
- Pincode
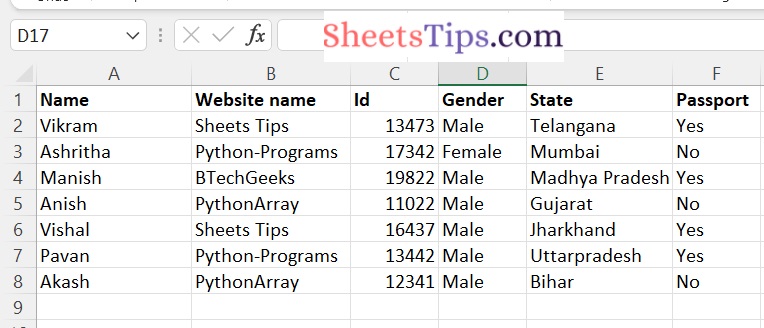
sampleExcelFile2.xlsx:
This file contains 6 columns with 7 unique student details. The following are the column names:
- Name
- Website name
- Id
- Gender
- State
- Passport
read_excel() function:
The read excel method accepts two arguments: sheet name and index col. sheet name defines the sheet from which the data frame should be created, and the index col gives the title column.
Approach:
- Import the pandas module using the import Keyword.
- Read the first excel file using the read_excel() function by passing the argument file path of the first excel file and store it in a variable.
- Read the second excel file using the read_excel() function by passing the argument file path of the second excel file and store it in a variable.
-
Iterate in the Columns Names of the both excel sheets using the for loop.
- Here i(iterator) represents the column Names of the first excel sheet.
- Here j(iterator) represents the column Names of the second excel sheet.
- We iterate in both excel sheets using the zip() function by passing the arguments first and the excel files.
- Take two empty that stores the column names of the excel Files and store them in two variables.
- Creating empty lists to append the column values.
- Iterating in columns values of the two excel files using the zip() function by passing the arguments first and excel files corresponding column names.
- Append the corresponding first column name values to the firstExcelColumns list using the append() function by passing the argument iterator value.
- Append the corresponding second column name values to the secondExcelColumns list using the append() function by passing the argument iterator value.
- Sort the corresponding firstExcelColumns list using the sort() function.
- Sort the corresponding secondExcelColumns list using the sort() function.
- Iterating the firstExcelColumns and secondExcelColumns list using the zip() and range() functions.
- Check if the firstExcelColumns name is not equal to secondExcelColumns using the if conditional statement.
- If it is true then print the Column name and Row Number.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the Implementation:
# Import the pandas module using the import Keyword
import pandas as pd
#Reading two Excel Sheets
# Read the first excel file using the read_excel() function
# by passing the argument file path of the first excel file and store it in a variable.
excelFile1 = pd.read_excel("sampleExcelFile1.xlsx")
# Read the second excel file using the read_excel() function
# by passing the argument file path of the second excel file and store it in a variable.
excelFile2 = pd.read_excel("sampleExcelFile2.xlsx")
# Iterate in the Columns Names of the both excel sheets using the for loop
# Here i(iterator) represents the column Names of the first excel sheet
# Here j(iterator) represents the column Names of the second excel sheet
# We iterate in the both excel sheets using the zip() function by passing the arguments first and excel files
for i,j in zip(excelFile1,excelFile2):
# Take two empty that stores the columns names of the excel Files and store them in two variables.
# Creating empty lists to append the columns values
firstExcelColumns,secondExcelColumns =[],[]
# Iterating in columns values of the two excel files using the zip() function
# by passing the arguments first and excel files corresponding column names
for m, n in zip(excelFile1[i],excelFile2[j]):
# Append the corresponding first column name values to the firstExcelColumns
# list using the append() function by passing the argument iterator value
firstExcelColumns.append(m)
# Append the corresponding second column name values to the secondExcelColumns
# list using the append() function by passing the argument iterator value
secondExcelColumns.append(n)
# Sort the corresponding firstExcelColumns list using the sort() function
firstExcelColumns.sort()
# Sort the corresponding secondExcelColumns list using the sort() function
secondExcelColumns.sort()
# Iterating the firstExcelColumns and secondExcelColumns list using the zip() and range() functions
for m, n in zip(range(len(firstExcelColumns)), range(len(secondExcelColumns))):
# Check if the firstExcelColumns name is not equal to secondExcelColumns using the if conditional statement
if firstExcelColumns[m] != secondExcelColumns[n]:
# If it is true then print the Column name and Row Number
print('Column name : \'{}\' and Row Number : {}'.format(i,m))
Output:
Column name : 'Website name ' and Row Number : 0 Column name : 'Website name ' and Row Number : 1 Column name : 'Website name ' and Row Number : 2 Column name : 'Website name ' and Row Number : 3 Column name : 'Website name ' and Row Number : 4 Column name : 'Website name ' and Row Number : 5 Column name : 'Name' and Row Number : 0 Column name : 'Name' and Row Number : 1 Column name : 'Name' and Row Number : 2 Column name : 'Name' and Row Number : 3 Column name : 'Name' and Row Number : 4 Column name : 'Name' and Row Number : 5 Column name : 'Age' and Row Number : 0 Column name : 'Age' and Row Number : 1 Column name : 'Age' and Row Number : 2 Column name : 'Age' and Row Number : 3 Column name : 'Age' and Row Number : 4 Column name : 'Age' and Row Number : 5 Column name : 'City' and Row Number : 0 Column name : 'City' and Row Number : 1 Column name : 'City' and Row Number : 2 Column name : 'City' and Row Number : 3 Column name : 'City' and Row Number : 4 Column name : 'City' and Row Number : 5 Column name : 'Pincode' and Row Number : 0 Column name : 'Pincode' and Row Number : 1 Column name : 'Pincode' and Row Number : 2 Column name : 'Pincode' and Row Number : 3 Column name : 'Pincode' and Row Number : 4 Column name : 'Pincode' and Row Number : 5

