In this tutorial, we’ll look at how to use Python to convert any Dates in Spreadsheets.
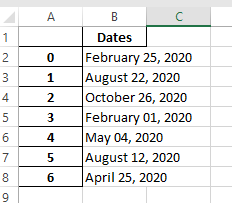
Let us take an example of demo.xlsx excel spreadsheet that is shown below:
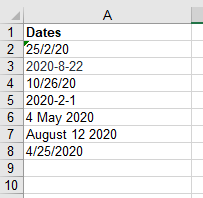
This file contains a single column called ‘Dates,’ which stores random dates from 2020 in various formats.
to_datetime() Method: To conduct date and time operations, we must first convert the column to a datetime data type.
dt.strftime() Method:
Then, using a value of “%Y-%m-%d” we utilise the dt and strftime methods to tell Python how to format the date. The example we used here is “% Y-% m-% “, where % Y is the whole year, % m is the month with two digits, and % d is the day with two digits.
- Python – Convert excel serial date to datetime
- Python Program to Convert Excel to PDF
- Convert CSV to Excel using Pandas in Python
Program to Convert any Dates in Spreadsheets in Python
Example1
Approach:
- Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword.
- Read the file and indicate which column contains the Dates using the read_excel() function and store it in a variable.
- (here the file has only 1 column, hence we didn’t specify Dates column).
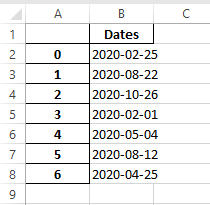
- Convert the Dates column in the above file to YYYY-MM-DD format using the to_datetime,dt.strftime functions.
- And store the formated dates output into another Excel file using the to_excel() function.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Read the file and indicate which column contains the Dates using the read_excel() function
# and store it in a variable
# (here the file has only 1 column, hence we didn't specify Dates column)
demo_file = pd.read_excel("demo.xlsx")
# Convert the Dates column in the above file to YYYY-MM-DD format using the to_datetime,dt.strftime functions
# And store the formated dates output into another Excel file using the to_excel() function.
demo_file["Dates"] = pd.to_datetime(
demo_file["Dates"]).dt.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
demo_file.to_excel("demo_format.xlsx")
Output:
Different date formats:
Example: Monday, 16 May, 2020, 5:00 PM
“%A, %B %d” -> “Monday, May18”
“%d-%b-%y” -> “16-May-20”
“%d/%m/%Y” -> “16/05/2020”
“%b %d, %Y” -> “May 16, 2020”
| Directive | Description | Example |
| %a | Weekday as locale’s abbreviated name | Sun, Mon,….,Sat(en_US);
So, Mo,……, Sa(de_DE) |
| %A | Weekday as locale full name | Sunday, Monday, Tuesday,….., Saturday |
| %w | Weekday as a decimal number, where 0 represents Sunday and 6 represents Saturday | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 |
| %d | The month’s day as a zero-padded decimal number | 01, 02, 03, …………,31 |
Example2:
Now let us change the date format as shown below for the same dataset
Format:
"%d %b, %Y" --> "16 May, 2020"
# Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Read the file and indicate which column contains the Dates using the read_excel() function
# and store it in a variable
# (here the file has only 1 column, hence we didn't specify Dates column)
demo_file = pd.read_excel("demo.xlsx")
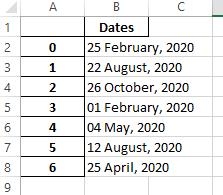
# Convert the Dates column in the above file to "D MMMM, YYYY" format using the to_datetime,dt.strftime functions
# And store the formated dates output into another Excel file using the to_excel() function.
demo_file["Dates"] = pd.to_datetime(
demo_file["Dates"]).dt.strftime("%#d %B, %Y")
demo_file.to_excel("demo_format.xlsx")
Output:
Example3
Now let us change the date format as shown below for the same dataset:
Format:
"%B %d, %Y" --> "May 16, 2020"
# Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Read the file and indicate which column contains the Dates using the read_excel() function
# and store it in a variable
# (here the file has only 1 column, hence we didn't specify Dates column)
demo_file = pd.read_excel("demo.xlsx")
# Convert the Dates column in the above file to "MMMM D, YYY" format using the to_datetime,dt.strftime functions
# And store the formated dates output into another Excel file using the to_excel() function.
demo_file["Dates"] = pd.to_datetime(
demo_file["Dates"]).dt.strftime("%B %d, %Y")
demo_file.to_excel("demo1_format.xlsx")
Output: