The dataset may not always be available in CSV format. As a result, Pandas includes functions for converting datasets in different formats to Data frames. The format of an excel file is ‘.xlsx’.
Before we begin, we must first install a few libraries as shown below:
pip install pandas pip install xlrd
We must use the pandas.read_excel() function to import an Excel file into Python using Pandas.
Syntax:
pandas.read_excel(io, sheet_name=0, header=0, names=None,….)
Return Value: It returns a Dataframe or a dictionary of Dataframes.
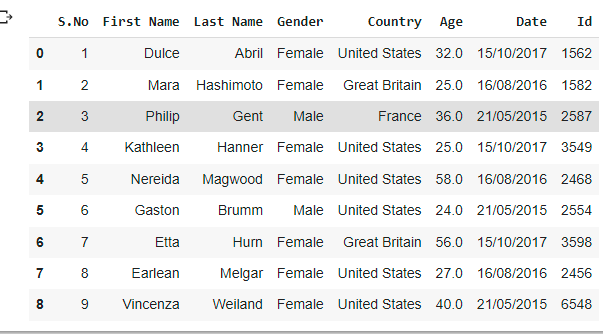
Let us take an example of demo.xlsx excel spreadsheet as shown below:
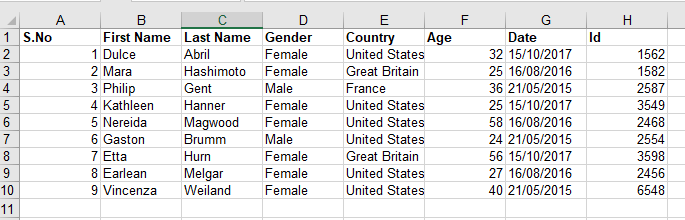
- How to Convert PDF File to Excel File using Python?
- Python Split given List and Insert in Excel File
- Python Program to Convert an HTML Table into excel
How to Import an Excel File into Python using Pandas?
Example1: Reading an Excel file
Approach:
- Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword.
- Read the excel file using the read_excel() function and store it as a DataFrame.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Read the excel file using the read_excel() function and
# store it as a DataFrame
data_frme = pd.read_excel('demo.xlsx')
data_frme
Output:
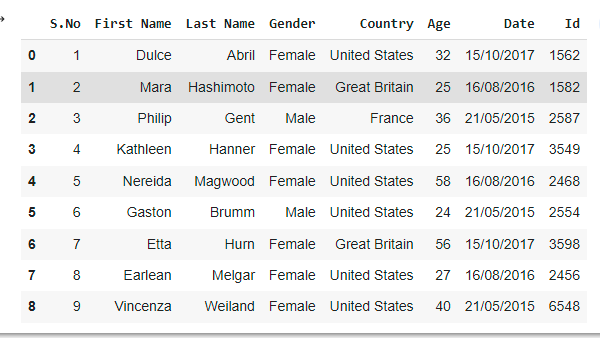
Example2: Selecting a specific column
Approach:
- Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword.
- Select a specific column of the excel file using the index_col by passing the column index as an argument to it.
- The Exit of the Program.
# Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Select a specific column of the excel file using the index_col by passing the
# column index as an argument to it
data_frme= pd.read_excel("sample.xlsx",
index_col = 0)
data_frme
Output:
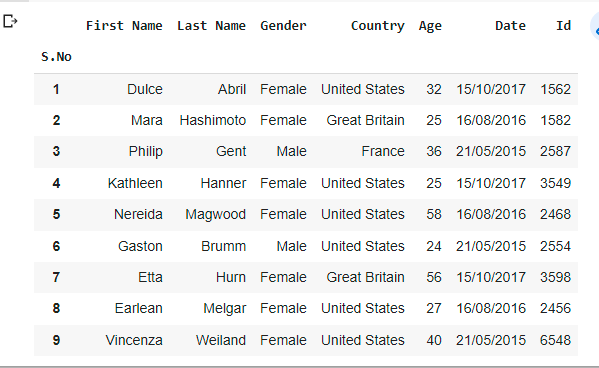
Example3:
If we don’t want the initial heading of the columns, you can change it to indexes by using the “header” argument.
# Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Read the excel file using the read_excel() function by passing the
# file name and header= None as the arguments to it.
# (It modifies the header with indexes)
# store it as a DataFrame
data_frme= pd.read_excel('demo.xlsx',
header = None)
data_frme
Output:
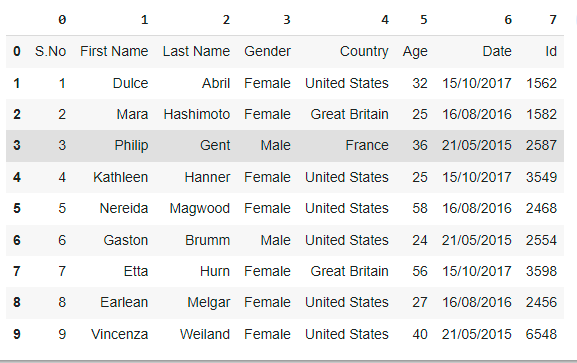
Example4: Changing the datatype of columns
If we wish to modify or change the data type of a certain column, use the “dtype” argument.
# Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Change the datatype of coulums(Gender, Age) using the dtype parameter
# and store it in a variable
data_frme= pd.read_excel('demo.xlsx',
dtype = {"Gender": str,
"Age":float})
data_frme
Output:
Example5:
If we have unknown values, you can handle them with the “na_values” argument. It will convert the previously specified unknown values to “NaN.”
# Import pandas module as pd using the import keyword
import pandas as pd
# Convert the unknown values to NaN using the na_values argument
data_frme= df = pd.read_excel('demo.xlsx',
na_values =['Mara',
'Philip'])
data_frme
Output:
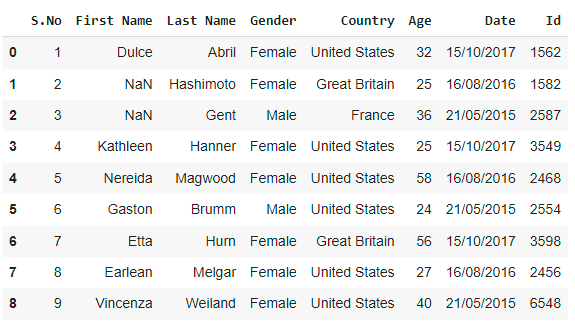
Here we converted unknown/unwanted data (Mara,Philip) to NaN values.
Also Read: Python: Print items of a dictionary line by line (4 ways)
